AC010521-Hemostatic-HA-1-800
Trauma is the leading cause of death for Americans age 45 or younger. Hemorrhage Is the leading cause of preventable death in combat trauma. It is the secondary cause of death in civilian trauma.
A significant number of deaths due to hemorrhage occur before arrival at the hospital. The only thing more tragic than a death from hemorrhage is a death that could have been prevented.
Hypovolemic shock occurs where there is an acute fluid or blood loss in the body. It is a life threatening emergency associated with high mortality. Hypovolemic shock in adults is most often secondary to rapid blood loss (hemorrhagic shock). The effects rapidly become irreversible. It causes inability of the heart to pump the essential blood needed to the body, resulting in multiple organ failure.
Tourniquets have emerged as the standard of care in the tactical environment due to their ease of use, rapid application, and complete stoppage of blood loss. Current protocol considers the tourniquet an initial lifesaving intervention to control massive hemorrhage from an extremity. You should always carry one.
Not all wounds are amenable to tourniquet use. For compressible hemorrhage not amenable to tourniquet use or as an adjunct to tourniquet removal (if evacuation time is anticipated to be longer than two hours) a hemostatic agent, Tactical Combat Casualty Care (TCCC) Guidelines specify the application of a hemostatic agent in conjunction with the application of least three minutes of direct pressure.
Hemostatic agents are primarily employed to control life-threatening bleeds in the junctional areas of the body. (think of where body parts meet the trunk, i.e., base of the neck, armpits and groin). They’re NOT for use in penetrating thoracic or head trauma. They can be used for deep lacerations if pleural or peritoneal space hasn’t been breached.
Hemostatic agents have become popular in Tactical Emergency Medical Support (TEMS) because they are designed to work to promote hemostasis quicker than traditional direct pressure will. This is not to say that they are without controversy. While the general consensus is that these agents are a valuable adjunct to achieving hemostasis, there are those who see little or no value their use.
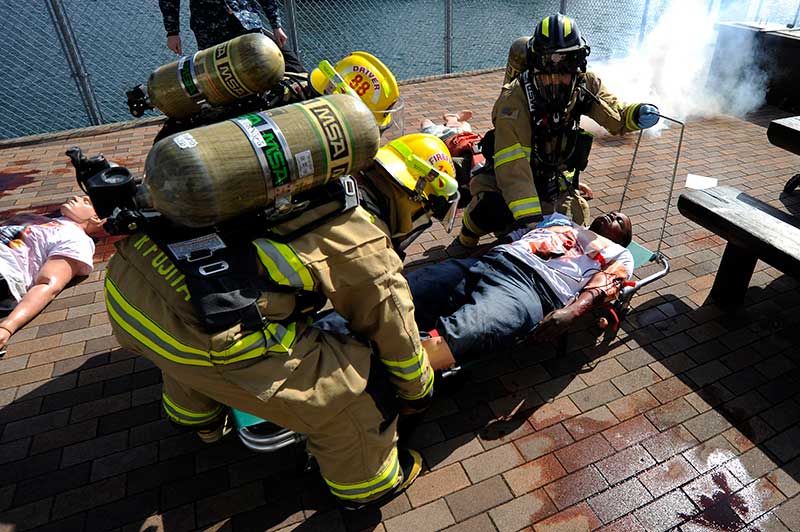

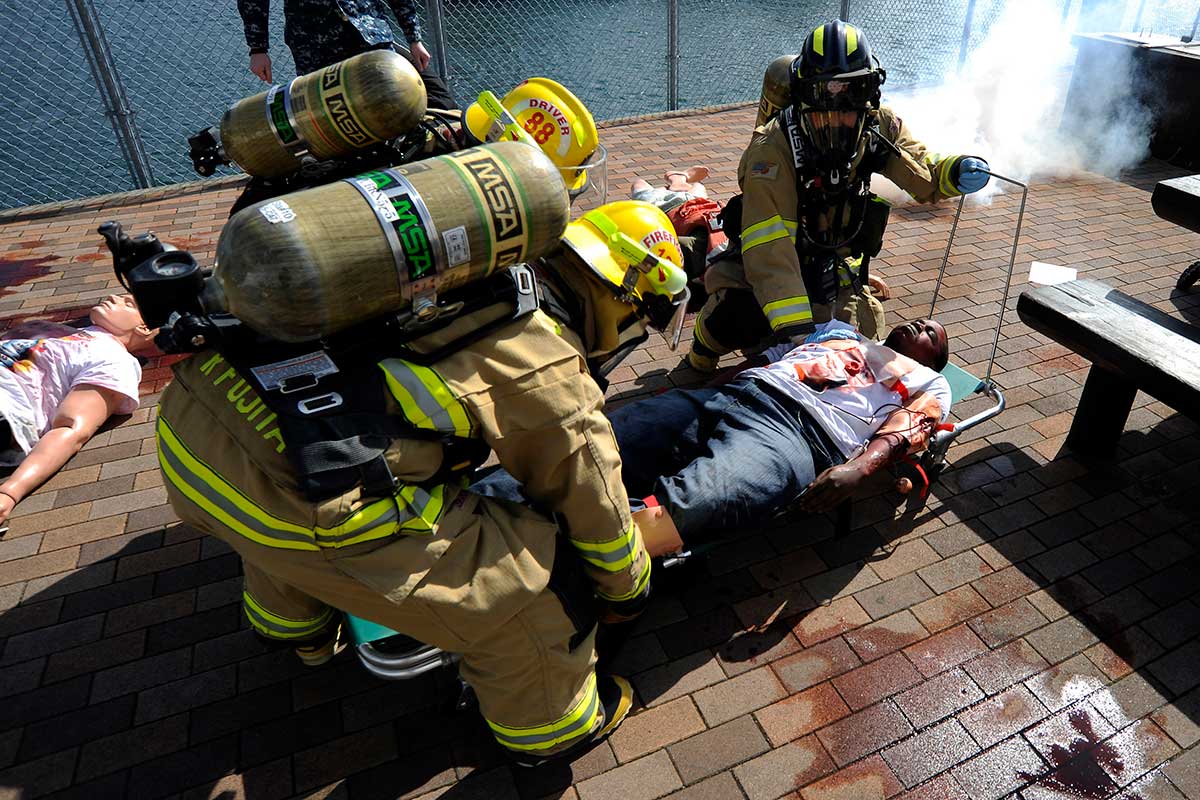
Firefighters transport “patient” to ambulance during an antiterrorism training exercise. Hemorrhage is the leading cause of preventable death in combat trauma and the secondary cause of death in civilian trauma.
When it comes to these products, they must be thought of as adjuncts to the means to the end. No hemostatic agent alone can stop significant bleeding. All must be coupled with pressure and the principles of blood flow and blood clotting. When applied in conjunction to pressure, then the product can certainly accelerate clotting and thus slow and stop bleeding. Such agents work great as the material used to pack deep wounds and when combined with surface pressure, the results are commonly favorable.
Achieving hemostasis can be a major problem for some individuals, particularly those who take “blood thinners” (anticoagulants) such as Warfarin) or Clopidogrel), those who suffer from inherited or acquired bleeding or clotting disorders. The blood in these individuals does not clot quickly. Even the smallest cut can be a real problem. Hemostatic agents may be a valuable adjunct to achieving homeostasis in these patients.
This doesn’t mean they hemostatic agents are without controversy. While the general consensus is that these agents are a valuable adjunct to the effort to stop blood loss, some see less value in their use.
The overall answer may be that, when it comes to these products, they must be thought of as an addition to the means to the end. No hemostatic agent alone can stop significant bleeding. All must be coupled with direct pressure and the principles of blood pressure, blood flow, blood clotting, and most importantly, proper training.
There are a variety of hemostatic products that are available. All of them perform well on heavy bleeds when used as intended. The latest generation of hemostatic products perform significantly better than earlier generations. The shelf life of these products is related to sterility, not efficacy.
I recommend going with a hemostatic product that is employed by the U.S. military in combat. Z-Medica® OuikClot® Combat Gauze®, Celox® Gauze and HemCon® ChitoGauze® and RevMedx® XSTAT® are Tactical Combat Casualty Care (TCCC) recommended hemostatic adjuncts for all five branches of the U.S. military. Although not yet on the TCCC list, RevMedx XGAUZE® is also currently used by the U.S. military and standard issue in the U.S. Army Combat Medic Kit. They work by different modalities.
QUIKCLOT COMBAT GAUZE
QuikClot Combat Gauze is impregnated with kaolin, a material that helps the blood to clot. It has been found in lab studies to control bleeding that would otherwise be fatal. Unlike previous generations of QuikClot products, the kaolin-based 3rd Generation QuikClot doesn’t cause an exothermic reaction.
Kaolin is a naturally occurring inert aluminosilicate clay mineral that initiates the clotting process. Kaolin is utilized routinely in reagents that are used to assay blood clotting times by clinical laboratories that follow procedures that are published by the College of American Pathologists.
Kaolin-based QuikClot gauze has been subjected to safety and efficacy studies that were performed by the U.S. Amy Institute for Surgical Research (USAISR) and the Naval Medical Research Center. As a direct result of the USAISR studies, the TCCC Guidelines were revised to make Combat Gauze the first line of treatment for life-threatening hemorrhage on external wounds that are not amenable to a tourniquet.
QuikClot has been accepted by all branches of the U.S. military. QuikClot Bleeding Control Dressing utilizes the same inorganic kaolin component as QuikClot Combat Gauze, which is used by the US military.

For bleeding that can’t be stopped only by compression and isn’t amenable to tourniquet placement, a hemostatic (clotting) agent should be used (with certain caveats). QuikClot Combat Gauze is one of the hemostatic agents recommended by TCCC. LE version is shown.
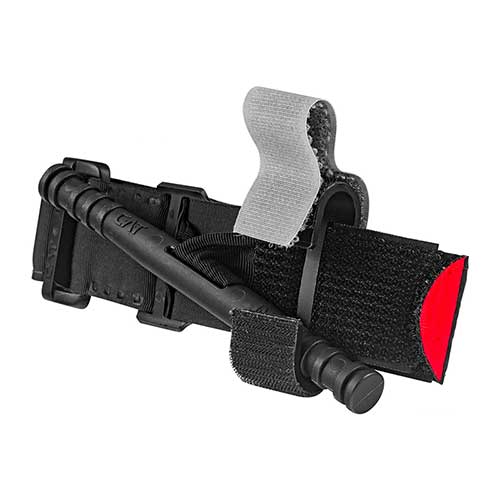

Tourniquets have emerged as the standard of care in the tactical environment, but not all bleeding is amenable to tourniquet placement. Combat Application Tourniquet (C-A-T) Gen 7 shown is one of the tourniquets recommended by TCCC.
CELOX GAUZE AND CHITOGAUZE
Celox Gauze and ChitoGauze hemostatic products are chitosan-based. Chitosan is a natural polysaccharide that is extracted from the shells of crustaceans and highly purified. It is non-allergenic.
Chitosan is manufactured by treating shrimp and other crustacean shells with an alkaline substance, such as sodium hydroxide. It forms a gel-like clot when it comes into contact with blood. The chitosan binds red blood cells and platelets on the dressing’s surface which provides localized clotting independently from the normal clotting cascade.
Chitosan has been shown to work equally well when there is a problem with clotting, such on hypothermic bleeding found in severe trauma. As casualties lose blood, their body temperature drops and blood no longer clots normally. In addition to its hemostatic properties Chitosan also is antibacterial.
A study published in the October 2011 Military Medicine reported the safety of the HemCon bandage (ChitoGauze) in shellfish allergic patients. Participants who demonstrated specific shellfish allergies underwent a bandage challenge. All participants tolerated the HemCon bandage without reaction.
This was the first study demonstrating the safety of this bandage in shellfish allergic subjects. Although this study dealt specifically with the HemCon bandage the results can be extrapolated to other Chitosan bandages.
XGAUZE & XSTAT
XGAUZE and XSTAT utilize small cellulose sponges that adsorb and rapidly expand on contact with blood to provide hemostatic pressure. They don’t require external compression, making them suitable for use on non-compressible wounds.
XGAUZE is the only self-expanding gauze on the market. Compressed sponges embedded in XGAUZE rapidly absorb blood and expand to ten times their original size. According to RevMedX, one expanded XGAUZE fills the same volume as three standard gauze dressings. It simplifies wound packing, reducing application time by 40% compared to standard gauze dressings.
XSTAT is an injectable wound treatment designed to immediately control hemorrhage from penetrating wounds, such as gunshot and knife wounds. It works by injecting the sponges directly into a wound cavity using a syringe-like applicator.
XSTAT is available in two applicator sizes: XSTAT 30 Gen 2 and smaller XSTAT 12. The XSTAT 12 is designed to treat life-threatening bleeding from penetrating wounds in junctional areas that may be too narrow to access with the larger XSTAT 30. The XSTAT12 is standard issue for SOCOM IFAKs, CASEVAC program and Medic/Corpsman Kit.
According to RevMedX, XSTAT can stop bleeding in seconds to stabilize injuries until patients reach an emergency facility.
FINAL THOUGHTS
Which of the products is best for field use? All of the companies can point to studies that demonstrate the superiority of their products over competing products. I think that answer to this is an unavoidable inherent variability in the studies. All of the products have been shown to work. All of the products are safe when used as intended, They will be irrigated out of the wound at the hospital.
The proper employment of a hemostatic agent can be a lifesaver. A hemostatic dressing should be in every trauma kit. It is not complete without one.
That being said, it is important to keep in mind that a review of available literature shows that none of the hemostatic agents have proven superior under all conditions and in all wound types. Proper wound packing and pressure may be more important than the use of a hemostatic agent in small penetrating wounds.
Having the necessary tools, while essential, is only part of the equation. Equipment is only as good as your training. Basic emergency medical training should cover the entire spectrum of lifesaving skills. And like shooting, they’re perishable skills. Emergency medical training should be part of the basic skill sets of every firearms owner. In fact, it should be part of the basic skill sets of everyone. The time to learn how to use a trauma kit isn’t when someone is bleeding out.
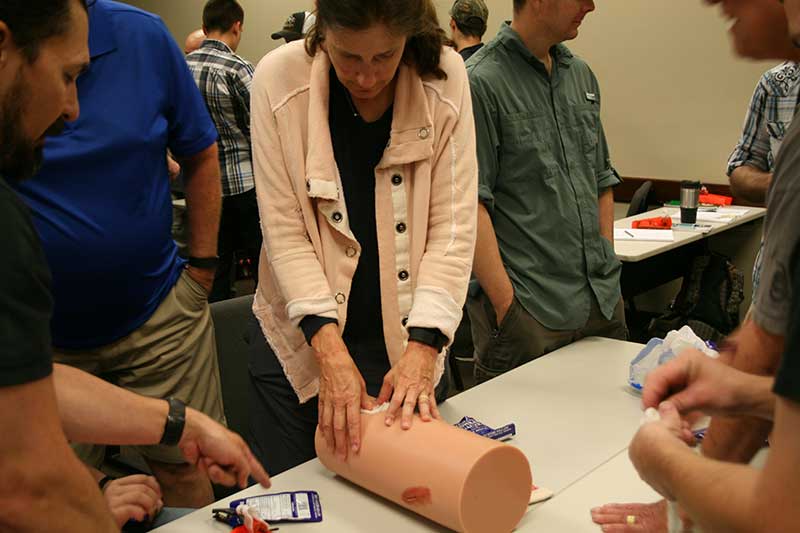
Training is essential. Student shown practicing wound packing under watchful eye of instructor Kerry Davis during Dark Angel Medical Direct Action Response Training (D.A.R.T.) course that author took.
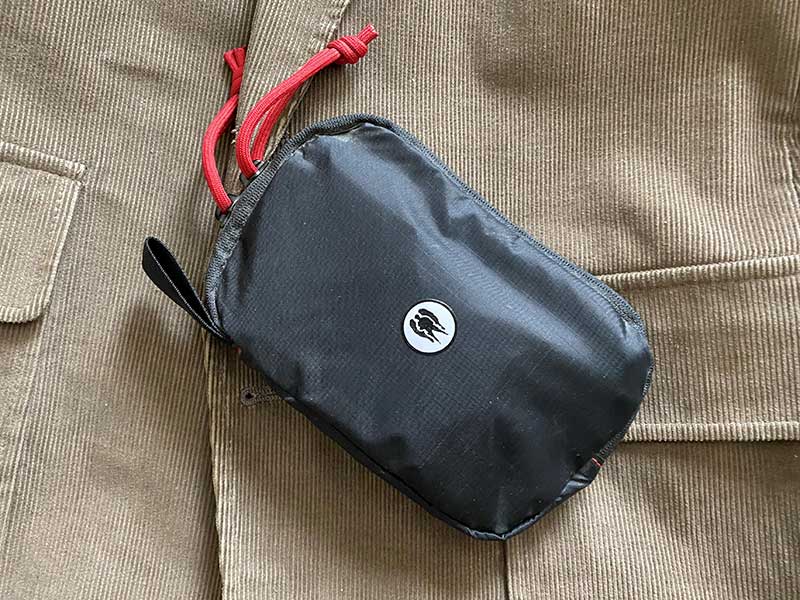

Dark Angel Medical Pocket D.A.R.K. Mini PLUS is an outstanding low-profile trauma kit for everyday carry. As with all Dark Angel Medical products, it has been very well thought out. It’s designed for when you just don’t have the room for a larger kit but don’t want to sacrifice the ability to “Stop the Bleeding and Start the Breathing.”
The National Association of Emergency Medical Technicians (NAEMT) and STOP THE BLEED® are excellent resources that can direct you to courses in your area.
Dark Angel Medical offers their outstanding two-day Direct Action Response Training (D.A.R.T.) course at various locations around the country. All participants receive BCON (Bleeding Control) certification from the American College of Surgeons. I have taken the D.A.R.T. course and highly recommend it.
Dark Angel Medical also offers a free online introductory course designed to teach the basics of bleeding control, as well as numerous trauma kits and components.
The online learning platform Deployed Medicine is another useful resource. It’s used by the Defense Health Agency (DHA) “to trial new innovative learning models aimed at improving readiness and performance of deployed military medical personnel.” Deployed Medicine also offers free apps for iOS and Android devices, available on the App Store and Google Play. And you don’t have to be a member of the military take advantage of it.
DARK ANGEL MEDICAL
www.darkangelmedical.com
DEPLOYED MEDICINE
www.deployedmedicine.com
STOP THE BLEED
www.stopthebleed.org














